How Does An AI-Operated Restaurant Even Work?
Artificial intelligence seems to be everywhere these days, from flashy tech startups to healthcare giants. The world of food is certainly no exception. From generating cocktail art to developing cookie recipes, AI has made splashy headlines for its use in the kitchen. Soon, it might even be behind your favorite dinner. That's right — restaurants across the country are rolling out automated programs that do everything from preparing food to taking orders.
In many cases, restaurants use AI-powered tools to improve behind-the-scenes business processes like logistics, inventory, and staffing. However, as AI progresses, it's starting to be used more and more in day-to-day operations. Some companies are creating robotic hardware to automate cooking processes, while others are focusing on software that handles orders. Outliers are attempting to build restaurant models from scratch, maximizing the amount of technology and minimizing traditional labor. In reality, most AI-operated kitchens work through a mix of robots, voice technology, and usually the helping hands of actual human beings.
Robots in the kitchen
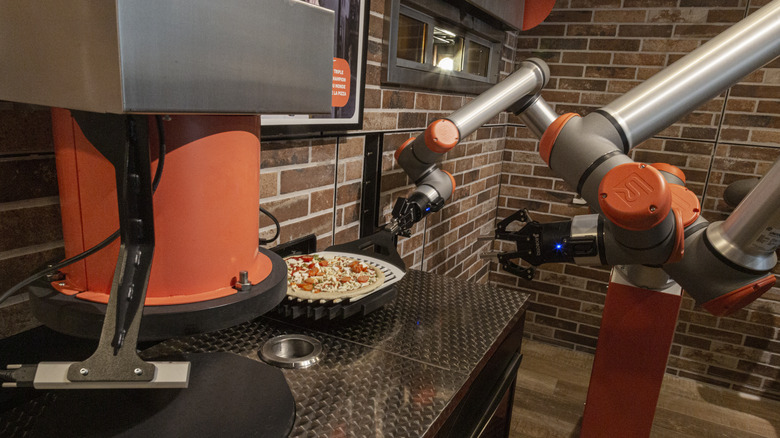
When it comes to making food, robots are king. Or at least that's what several futuristic restaurants hope. Sweetgreen, a fast food joint that specializes in serving quick salads, began employing the Infinite Kitchen, a restaurant powered almost entirely by robots. The Sweetgreen system utilizes robots to add salad ingredients to bowls as they move along a conveyor belt. Employees will add garnishes to completed dishes and are also present to greet guests and help them place orders. Sweetgreen operates two Infinite Kitchens — in Illinois and California — but plans to eventually implement them into every new location of the chain.
Some establishments are hoping to cut out human requirements altogether, running solely on machines. In a press release, CaliExpress by Flippy recently billed itself as "the world's first fully autonomous restaurant." The establishment, a product of the Cali Group, Miso Robotics, and PopID, serves french fries and burgers. While the restaurant does staff a small number of employees, the entire ordering process and every part of the cooking is completed at the hands of automated robots. Guests are able to watch this process, which includes a grill robot that grinds fresh beef for each order and a robotic fry station known as Flippy. CaliExpress claims that the technological efficiencies in this system allow them to serve "freshly made burgers based on a wagyu blend" at competitive market prices.
Generative language models
Robots may take the lead on food prep, but other AI-powered restaurant operations rely on generative language technology. Last year, Wendy's rolled out a Google-powered AI drive-thru that utilizes the tech giant's Vertex AI model. This AI model is capable of interacting with guests and taking verbal orders. It is even built to handle the intricate and complex requests that are common at drive-thru windows and is programmed to respond to a number of frequently asked questions. The software is also capable of holding a conversation while you place an order.
Unlike CaliExpress and Sweetgreen, Wendy's partnership with Google is not focused on improving processes in the kitchen. Instead, Wendy's noted in a press release that the system is designed to create efficiencies in the ordering process, which will allow the employees to maximize their time cooking and completing orders. So while customers may notice that an actual human isn't talking to them in the drive-thru, their overall Wendy's experience will likely remain pretty consistent.