What Are The Differences Between Beyond Meat And Impossible Burger?
It's fair to say that faux meat products are booming in popularity with the United States' meat substitute market projected to grow by nearly 12% between 2021 and 2028, as reported by The Brainy Insights. This growth is due to a number of complicated and interrelated reasons. However, common themes include consumer desires to reduce their environmental impact, improve their health, and limit contributions to poor animal welfare standards, per Vox. Meat substitutes play a vital role due to their unique ability to satisfy these wants without forcing individuals to sacrifice the flavors, textures, and meals they've always enjoyed.
Beyond Meat and Impossible Foods are two companies that have come to define the faux meat market. Both of these companies currently have a range of products to their names; however, they originally came to prominence by satiating the public's desire for a meat-free — but still meat-like — burger. Solving this decades-long conundrum was a process that each company tackled differently. As such, the products created — the Beyond Burger and the Impossible Burger — are wholly unique, with their own positives and negatives. Read on to discover more about the disparities that make these two industry-altering products — and the companies that make them — so distinct.
Different plant proteins are used in the two products
Both the Beyond Burger and the Impossible Burger are constituted from a range of proteins, fats, binders, and starches to create a product that replicates the taste, appearance, and texture of a beef burger. As ultra-endurance athlete and vegan podcast host Rich Roll highlighted in a blog for Forks Over Knives in 2014, the main preoccupation people have with vegan foods and diets is whether they contain sufficient amounts of protein. It is quite natural then that both the Beyond Burger and the Impossible Burger are clearly labeled as having 19 grams of protein per burger, which is the amount normally associated with a 20% fat beef burger.
But while the amount of protein is uniform between the two burgers, the source of this vital nutrient does differ. As reported by Beyond Meat, Beyond Burger's protein is made from a mix of pea protein and rice protein. The former is seen as a fantastic vegan alternative to meat-based proteins because it contains all nine of the essential amino acids humans require, as per Texas Health. By comparison, Impossible Burger relies on protein from both soy and potato extract, with the former also containing all nine essential amino acids, alongside a range of vitamins, minerals, and nonessential amino acids, as reported in Soybean for Human Consumption and Animal Feed.
Impossible Burger tastes a lot more like meat
Soy not only provides the Impossible Burger with a robust source of amino acids, but it also gives the product its so-called "secret ingredient" — soy leghemoglobin. When heated, soy leghemoglobin breaks down to produce heme which, as explained by the American Society for Microbiology, are the proteins responsible for imparting the meaty flavor associated with animal muscle. By sourcing soy leghemoglobin from soybean roots and using yeast to produce it in vast quantities, Impossible Foods has access to a reliable and sustainable source of heme. This is of vital importance as it is fundamental to the Impossible Burger. First and foremost, heme imparts a flavor just like meat, which has allowed the Impossible Burger to gain notoriety as the meatiest of the faux meats. It also produces a pink color and helps the burger "bleed" (via The Verge). When combined, the meaty flavor and bloody appearance have seen the Impossible Burger receive rave reviews from vegans, vegetarians, and meat eaters alike, as per BBC Good Food.
On the other hand, the Beyond Burger recipe does not include heme. The company chose to avoid genetically modified ingredients in favor of combining other ingredients and manipulating them to produce a similar result. For example, the Beyond Burger "bleeds" due to beetroot juice being incorporated into the patty, as reported by The Guardian. However, the Beyond Burger struggles to achieve the same meaty taste as the heme-rich Impossible Burger.
The Beyond Burger has been around longer
As per Fast Company, despite the huge splash the Impossible Burger made upon its initial release in a few high-end restaurants, the Beyond Burger is still the name synonymous with meat-free burgers. This is largely due to the simple fact that the Beyond Burger was made available to the public sooner. The first iteration of the Beyond Burger was released in 2016 and was so markedly different from its competitors — the majority of them frozen patties that didn't even attempt to replicate meat — that it received stunning reviews (per Thrillist).
In contrast, the Impossible Burger only became available for retail in the autumn of 2019, per Impossible Burger via Businesswire. While also being met with fantastic reviews, it has struggled to reach as wide a consumer base as the Beyond Burger for a number of reasons. One is the simple fact that the market is more saturated than it was in the mid-2010s, with global publications, such as Fortune, suggesting that the faux meat industry has already peaked. Furthermore, safety concerns over the inclusion of genetically modified (GMO) heme have also limited the company's ability to bring the Impossible Burger to a wider, global audience.
The two burgers have slightly different environmental impacts
One reason consumers are turning to meat substitutes is because of the lesser environmental impact their production has when compared to beef burgers. As reported by NBC News, both the Beyond Burger and the Impossible Burger use significantly less land and water While also producing significantly less fossil fuel emissions than traditional beef burgers. When these two products are compared, the Beyond Burger has the edge over the Impossible Burger in water usage and fossil fuel emissions, While the roles are reversed when it comes to land use. However, the discrepancies between the two are minimal.
It is an undeniable fact that both the Impossible Burger and the Beyond Burger use significantly fewer resources to produce than traditional beef burgers. However, this does not mean that plant-based meat alternatives are the most environmentally-friendly dietary option available. Rather, the creation of products such as the Beyond and Impossible burgers creates more emissions than other alternatives as explained by Dr. Marco Springmann, a researcher at the Environmental Change Institute to CNBC. "While their processed products have about half the carbon footprint that chicken does, they also have five times more of a footprint than a bean patty," he said. "So Beyond and Impossible go somewhere towards reducing your carbon footprint, but saying it's the most climate-friendly thing to do — that's a false promise."
Impossible Burger initially launched through restaurants
Mania surrounded the retail release of the Impossible Burger in 2019 thanks to the rave reviews from chefs and customers. The burger gained popularity when it was featured on the menu of some of the most well-known restaurants in the U.S.
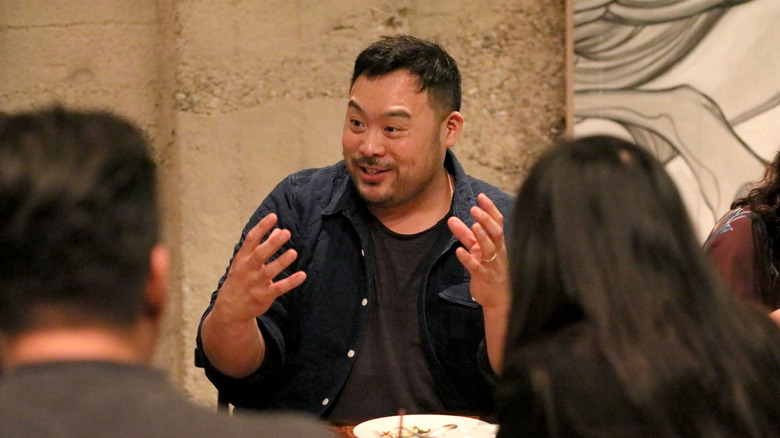
Momofuku Nishi, one part of genius David Chang's culinary empire, was the first to serve the Impossible Burger in 2016. Chang was enamored with the product, stating, "I was genuinely blown away when I tasted the burger. The Impossible Foods team has discovered how to re-engineer what makes beef taste like beef. We're always looking to support people who are making the best products in the best ways possible and to me, the Impossible Burger is one more example." Famously, the Impossible Burger even earned a spot on the menu at the Michelin-starred restaurant Public (per Fast Company).
The Beyond Burger took a much more traditional route into the industry, moving directly into retail and progressing into increasingly large distribution models. This sustained growth resulted in the company attracting several high-profile investors, such as Bill Gates. This is not to say that Beyond Meat hasn't utilized collaborations with restaurants to boost the popularity of its flagship product. On the contrary, as noted on Totally Vegan Buzz, partnerships with well-known restaurant chains — like TGI Fridays — have steadily boosted the status of the Beyond Burger.
Global availability of the two products widely differs
One of the most striking differences between the Impossible Burger and the Beyond Burger is the decisively different global distribution models currently employed by the two parent companies. Beyond Meat currently exports to more than 85 countries worldwide and has made serious commitments to providing Beyond Meat products — such as the Beyond Burger — to massive emerging markets like China (per Beyond Meat).
On the other hand, Impossible Food's global expansion has been severely limited, a fact that is partly due to fears over the GMO heme used in products like the Impossible Burger. As reported by both Food Navigator and Fortune, Britain, the European Union, and China — three potentially huge markets — have yet to approve the Impossible Foods manufactured heme. This means the company has been unable to sell the Impossible Burger to these markets, thus allowing Beyond Burger to globally expand with minimal competition. Impossible Foods' non-heme-containing products — such as Impossible Chicken Nuggets — are being released via restaurants in locations, such as the United Kingdom. Those at Impossible Foods undoubtedly hope these products will provide the brand with a foothold that will aid the launch of the Impossible Burger post-approval.
Impossible Burger contains genetically modified ingredients
The soy leghemoglobin used to impart meat-like characteristics in the Impossible Burger is somewhat controversial. This is in spite of the fact that the heme "farmed" by Impossible Foods is exactly the same as the heme that naturally occurs in all living beings, including humans. The controversy surrounding Impossible Foods' heme arises because it is made from genetically modified soybean plants, which then undergo a process of being replicated by genetically engineered yeast. As this is a novel process, many food safety agencies, such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), have had concerns that the heme produced could be an allergen or potentially be unsafe for human consumption (via The New York Times). Hence, the reason Impossible Foods has experienced much greater difficulty in bringing their product to market when compared with Beyond Meat, which uses more traditional ingredients, the safety of which has already been asserted.
In fact, the Beyond Burger — as with all Beyond Meat products — is marketed as being GMO-free, a fact which some believe makes it a more desirable investment prospect than the Impossible Burger. One such individual is Dan Gluck, a venture capitalist and private equity investor, who chose to invest in Beyond Meat for this very reason, as he explained to CNBC. "Beyond Meat's commitment to non-GMO ingredients was one of many factors that led us to conclude Beyond Meat was a better early stage investment opportunity versus Impossible," he commented.
Animal testing was used during the creation of the Impossible Burger
Proving that Impossible Foods' soy leghemoglobin is safe for human consumption has been a long and difficult road for the company. Perhaps the most challenging time throughout this process was when the FDA required scientific proof that the heme was nontoxic. This proof could only be provided through an experiment that tested the heme on rats.
As with any company that produces meat-free alternatives, avoiding animal suffering and cruelty is a large facet of the Impossible Burger's appeal. Indeed, as highlighted by British newspaper The Metro, there are many within the vegan community that believe testing on animals makes a product non-vegan. As such, the animal testing performed by Impossible Foods dealt a significant blow to the brand, although Pat Brown — CEO of Impossible Foods — highlighted why he deemed the process necessary for the long-term benefit of both the company and the wider world in an online statement released in August 2017.
Unsurprisingly, Beyond Meat has sought to distance itself from this controversy as much as possible, reminding the public at every opportunity that its products do not contain heme. The company also highlights that the Beyond Burger does not include any GMO ingredients and has never been tested on animals (via Beyond Meat).
Both companies have partnered with different fast food chains
One of the most effective ways of introducing the public to meat alternatives is to have the products available at extremely popular dining venues. In the United States — as in most countries — this means getting meat alternatives into fast-food chains, as these dominate the dining out industry, with sales that account for over 70% of total dollars spent on eating out, via Reuters. As such, competition between Impossible Foods and Beyond Meat to collaborate with the biggest fast-food brands has been fierce. The Impossible Burger has seen its biggest success at Burger King where the Impossible King and the Impossible Whopper have become regular menu fixtures (per Green Queen).
However, Beyond Meat claimed a collaboration with the biggest fast-food brand of all, McDonald's. The McPlant, which spotlights the Beyond Burger, has had great success in the U.K. and is now being widely released in the United States and Australia (per Vegconomist). This is seen as a big step for the fast-food behemoth, as many have suggested it was lagging behind competitors when it came to offering meatless alternatives. In a statement reported by Food Bev Media, Michelle Graham-Clare, one of McDonald's senior marketing officers, echoed this sentiment stating, "We are always looking for different ways to innovate and meet our customers' needs, and with McPlant we have a delicious plant-based burger that will appeal to everyone."
Impossible Burgers have been embroiled in a dispute about glyphosate
While the use of genetically modified soybean has caused controversy in some circles, the treatment these plants receive during growing has also brought some unwanted attention to the Impossible Burger. As reported by Food Revolution Network, the link between genetically engineered soy and the use of glyphosate — an herbicide — is well established, and the trace presence of glyphosate in food products is nothing new. However, in an article published on their website, Moms Across America suggested that glyphosate levels were found to be dangerously high in the Impossible Burger.
In a cutting rebuttal, Impossible Foods highlighted the scientific inaccuracies of the Moms Across America article, revealing instances of miscalculations and claims made without sufficient scientific backing. While Impossible Foods efficiently and effectively refuted the article, the claims made by Moms Across America illustrate another issue for the brand, namely that using GMO ingredients makes them a target for damaging attacks whether they be grounded in fact or not. Purely by virtue of being non-GMO, Beyond Meat suffers a great deal less from this type of information war, which can only benefit the brand in the long run.
Both companies plan to launch a vegan steak
While the Beyond Burger and the Impossible Burger are undoubtedly the flagship products of both companies, the meat alternative market means much more than just burger patties. Both have produced a range of sausage, chicken, and pork-like products. However, the biggest announcement for some time came via Beyond Meat CEO Ethan Brown, who stated that his company will be releasing a vegan steak. As highlighted by Veg News, the launch of this product heralds Brown's desire to create a comprehensive range of meat alternative products, with plans to disrupt the entire meat industry.
Not one to be left behind, Impossible Foods is working on a range of its own whole muscle-style products (per Vegconomist). Speaking to The Washington Post, CEO and founder of Impossible Foods Pat Brown suggested the Impossible Steak could be on the market sooner rather than later, saying, "I've seen and tasted some prototypes that would amaze you. But we're not going to launch a product on the market until we feel like it's something that a hardcore meat lover would say, 'This is awesome, I would definitely choose this.' [...] My guess is it will be well under two years [2023] until we have an amazing product or products on the market."
As a company, Beyond Meat is the first to see its popularity wane
As the Daily Mail highlighted, Beyond Meat's lucrative value on public markets has crashed from a peak of $14 billion to $2.3 billion. This massive drop in value has been caused by waning enthusiasm for the brand with a number of restaurants, including Del Taco and Dunkin', removing its products from their menus (per Bloomberg). Beyond Meat's struggles have been compounded by poor retail sales with surveys suggesting that young consumers may be less interested in meat alternatives than previously thought (via Barron's).
By comparison, Impossible Foods is going from strength to strength with rocketing retail revenue seeing the company named one of Time Magazine's most influential companies of 2022. This high level of brand confidence could not be coming at a better time for Impossible Foods as they look to take the company public (per City Index).